hv and lv cables | hv cable size chart hv and lv cables When it comes to electrical systems, understanding the difference between high-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) cables is crucial. Both cables play significant roles in power . 2015 – Rolex redesigns the Lady-Datejust line to now have larger 28mm cases. 2016 – Rolex discontinues the Datejust II line. 2016 – Rolex debuts the Datejust 41 collection, first in two-tone variants. 2017 – Rolex introduces steel and steel and white gold Datejust 41. Click here for our Ultimate Pricing Guide on the Rolex Datejust.
0 · types of hv cables
1 · hv electrical cables
2 · hv cable specifications
3 · hv cable size chart
4 · hv cable meaning
5 · hv cable data sheet
6 · hv cable catalogue
7 · cable insulation types chart
The Rolex Submariner Date 126610LV. Call it Starbucks, Cermit or Lunette Verte. But the Submariner is still one of the best luxury dive watches. 02/03/2022 | By .
In this post, we will learn some basic differences between two widely used electrical cables – HV (High Voltage) and LV (Low Voltage).Then the meter is connected between HV and earth point; and then LV and earth point to ge. When it comes to electrical systems, understanding the difference between high-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) cables is crucial. Both cables play significant roles in power .In this post, we will learn some basic differences between two widely used electrical cables – HV (High Voltage) and LV (Low Voltage).
When it comes to electrical systems, understanding the difference between high-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) cables is crucial. Both cables play significant roles in power distribution and transmission, but they have different purposes and distinct characteristics.LV cables are low voltage cables that are designed to transmit electrical power at voltage levels up to 1000 V. They are typically used for short-distance power transmission and distribution, such as within buildings and homes. In contrast, HV cables are high and medium-voltage cables that are designed to transmit electrical power at voltage .
The primary distinction between high-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) cables lies in their construction and insulation properties. High-voltage cables are designed with multiple semiconductor and shielding layers, which significantly exceed the .
Extra-High Voltage (EHV) and Ultra-High Voltage (UHV) Cable: are designed for long-distance and accommodating exceptionally high capacities. EHV cables can carry electrical currents above 230 kilovolts (kV), while UHV cables are . In a low-voltage (LV) plastic-sheathed cable with conductor cross-sections of up to 10 mm2 per conductor or in high-voltage (HV) cables (Figure 2), the lion’s share of the cross-sectional area is occupied by the insulating material.High Voltage (HV): between 45 kV and 230 kV. Extra High Voltage (EHV): from 230 kV and above. As a general rule, LV cables might be used in applications like fixed wiring; MV cables are critical power distribution (both for local grid power and for heavy-duty equipment); HV cables are aerial cables - overhead line for widescale power . Low and high voltage refers to the intensity at which electricity is sent through wires. Low voltage is less likely to cause damage or injury, while high voltage is more dangerous. While low voltage is generally safe, some safety measures should still be taken.
Two primary categories of these cables are high voltage (HV) cables and low voltage (LV) cables. Despite their shared purpose of conducting electricity, they are markedly different in terms of structure, materials, applications, and safety considerations. Low voltage cables are primarily used in residential, commercial buildings, and light industrial sites, medium voltage cables are suitable for urban distribution networks and industrial parks, while high voltage cables are used in transmission systems and large industrial facilities.In this post, we will learn some basic differences between two widely used electrical cables – HV (High Voltage) and LV (Low Voltage).When it comes to electrical systems, understanding the difference between high-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) cables is crucial. Both cables play significant roles in power distribution and transmission, but they have different purposes and distinct characteristics.
LV cables are low voltage cables that are designed to transmit electrical power at voltage levels up to 1000 V. They are typically used for short-distance power transmission and distribution, such as within buildings and homes. In contrast, HV cables are high and medium-voltage cables that are designed to transmit electrical power at voltage .
The primary distinction between high-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) cables lies in their construction and insulation properties. High-voltage cables are designed with multiple semiconductor and shielding layers, which significantly exceed the . Extra-High Voltage (EHV) and Ultra-High Voltage (UHV) Cable: are designed for long-distance and accommodating exceptionally high capacities. EHV cables can carry electrical currents above 230 kilovolts (kV), while UHV cables are . In a low-voltage (LV) plastic-sheathed cable with conductor cross-sections of up to 10 mm2 per conductor or in high-voltage (HV) cables (Figure 2), the lion’s share of the cross-sectional area is occupied by the insulating material.High Voltage (HV): between 45 kV and 230 kV. Extra High Voltage (EHV): from 230 kV and above. As a general rule, LV cables might be used in applications like fixed wiring; MV cables are critical power distribution (both for local grid power and for heavy-duty equipment); HV cables are aerial cables - overhead line for widescale power .
Low and high voltage refers to the intensity at which electricity is sent through wires. Low voltage is less likely to cause damage or injury, while high voltage is more dangerous. While low voltage is generally safe, some safety measures should still be taken.Two primary categories of these cables are high voltage (HV) cables and low voltage (LV) cables. Despite their shared purpose of conducting electricity, they are markedly different in terms of structure, materials, applications, and safety considerations.
tempi di attesa rolex submariner site orologi.forumfree.it
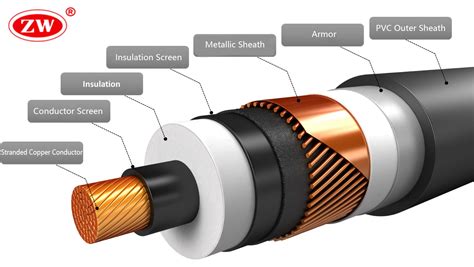
types of hv cables
hv electrical cables

Dial: Silver. Dial: Blue. 2010's. 2000's. Screw-Down Crown. Chronometer. Central seconds. }"> 778 listings including promoted listings. Sort by. Promoted. Rolex Datejust 36. 116234. C$ 11,798. Free shipping. US. Promoted. Rolex Datejust 36. RARE Salmon PINK Dial Super Jubilee Bracelet Stainless Steel Fluted Bezel. C$ 12,641. Free shipping. US.
hv and lv cables|hv cable size chart